My thesis: Thermal energy Vs. Gravitational pull
A brief history of scales
The first section (71 p.) of my book is my problem shooting concerning some of the physics problems that we up to now haven’t been able to solve satisfiedly. The different parts of the theory converge wholly according to Karl Popper’s criterions for what science is. The full theory is stringent, consistent and nearly entirely causal, but to bits and pieces at least coherent. There are many explaining graphs in this book. This is not a TOE or a GUT. What is?
________________________________________________________________________________________
Isaac Newton’s first law states that if a body is at rest or moving at a constant speed in a straight line, it will remain at rest or keep moving in a straight line at constant speed unless it is acted upon by a force.
A refutation of Isaac Newton’s first law:
- If a body is in orbital motion with a given sufficient apogee and perigee it will stay in orbit in an energy-conserving state if there aren’t any adequate amounts of accurately directed energy to it.
- Thermal energy [or electro-magnetism] is required direct to make matter move in straight or otherwise non-orbital trajectories.
Isaac Newton lived in a time when the Universe was considered static and constant by scientists. There was no beginning and no end, and the Universe certainly didn’t expand. Because of the false belief of the time that the Universe was static and constant he couldn’t, without revoking that common notion of the times, have concluded what I have concluded that actually the orbital motion is the energy-conserving motion which need a force to act upon a body for it to not keep orbiting around a larger object, and that it is the body which need an extra force of energy to leave a gravitational field. Newton didn’t consider a starting block for everything, like the Big bang. And what is the Big bang? It is added energy creating matter moving in straight trajectories. What is orbital movement? It is an energy-conserving motion for a body.
Albert Einstein came up with the theory of Relativity, his most important thesis, at the time when the Universe was still being considered static and constant. Einstein was unable to realize that a body must have an absolute speed limit below the speed of light, and because of this the Special theory of Relativity results in an all-out theoretic assumption about time dilation. Albert’s relativistic theory is a hypothesis somersault since his theory presupposes no speed limit for a body. Bodies in motion are considered to have relativistic speed by Einstein even though he didn’t believe in an absolute speed scale, or precisely because he didn’t believe in an absolute speed scale. And why wouldn’t he have considered bodies to have relativistic speed when the Universe was considered static and constant by him and his academic peers? Einstein’s theory is the blueprint of God’s construction, but Einstein didn’t consider the physical limitations of the building blocks for the structure of the universe.
The Author
________________________________________________________________________________________
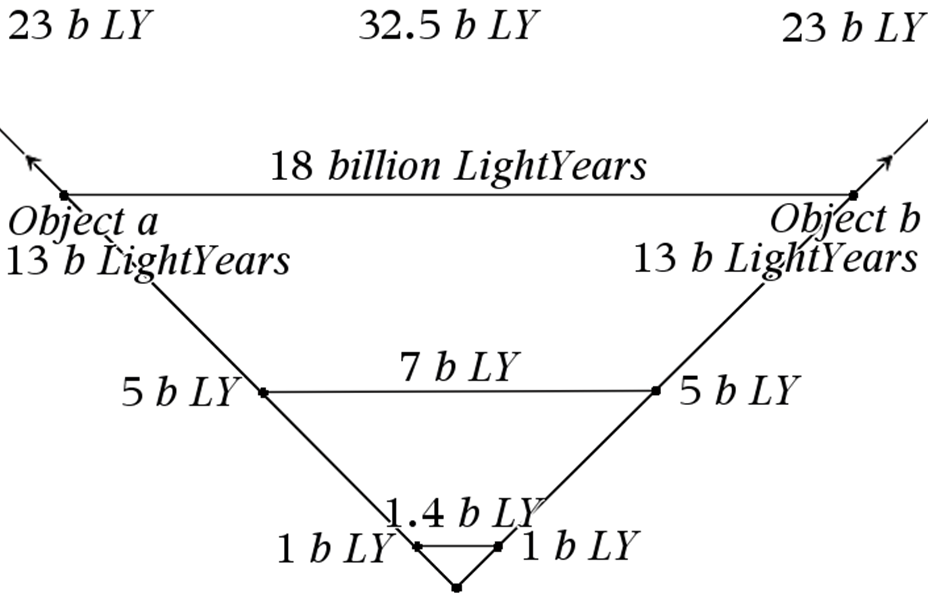
Let us slap the Pythagorean theorem onto the universe. In the image above, Objects a and b separate from each other in a ninety degrees angle at a speed well below the speed of light. The distance to the allegedly ascertained beginning of the universe is 13 billion lightyears for both Object a and Object b. The distance between Object a and Object b is then 18 billion lightyears. For the GN-z11 to be 32 billion lightyears apart from our galaxy, our galaxy must be 23 billion lightyears old. That is if we had been located at the edge of the universe as well as the GN-z11 had been located at the other edge. Obviously, we are not located at the edge of the visible universe. Since most of the objects in the universe have a velocity well below the speed of light, we should expect the universe to be much, much older than 13 (or perhaps 23) billion lightyears of age. Thirty-two billion lightyears are how far we can to date see, given that we are correct in our assessment of the distance from our galaxy to the GN-z11. Say that most of the galaxies in the known universe have a velocity of about 67 km per second.
67x60x60x24x365= 2,112,912,000 km or ~2 billion km per year.
So, if the assessment for the expansion speed is correct, then the age of the universe must be more than 300,000km/s x 0,00067km= 201 times greater than we expected.
23 billion lightyears x 201= 4.6 trillion years of actual age but supposedly more like double. Unless there was inflation.
If the universe is 4.6 trillion years old or rather twice that age, this would explain why the universe’s galaxies are not noticeably more densely packed the further back in time we look from Hubble and James Webb. With the aid of telescopes, we can see only a fraction of the universe. It would also explain why mega-structure formation of galaxies like “the Big ring” and “the Giant arc” can have developed in our universe. They had time!
I have imaginary set up the calculation according to the Pythagorean theorem for a right-angled triangle i.e., a2+b2=c2 and then calculated the square root of c2 to get a horizontal distance between Object a and Object b in the image above.
________________________________________________________________________________________
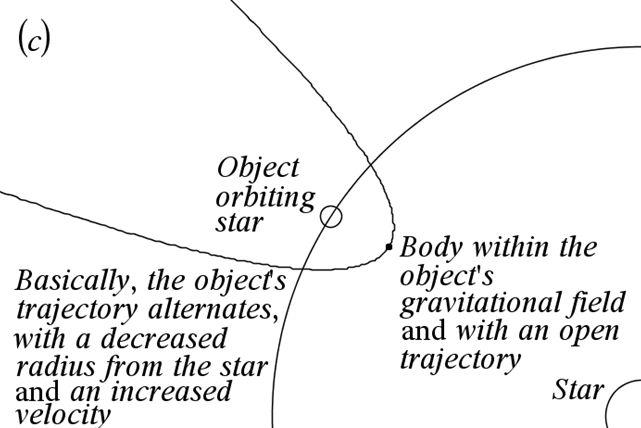
(a) A small body passing through a gravitational field changes course and accelerates. [Or it becomes caught in an orbit around the larger object.]
(b) The larger object’s velocity is decreasing. And the larger object’s orbit around the central star alternates a certain bit too, albeit this is very marginal and corresponds with the amount of energy the small body ”steals” as it pass through the large object’s gravitational field once. The large object’s trajectory alternates, basically with an increased radius from the star.
(c) One special circumstance is if the small body crosses paths (circumvents) with the larger object which is in orbit around a star or something. Then it will be the small body coming from outer space that loses energy in favor of the larger object, and the small body changes course with a decrease in speed for the small body which will appear to fall toward the larger object, if the body is within the larger object’s gravitational field. The large object’s trajectory alternates, basically with a decreased radius from the star, when the body is circumventing.
________________________________________________________________________________________
Teaser for my total rebuttal of Kurt Gödel’s Incompleteness theorem, also in the book.
So we have two statements:
- A means that A is unprovable
- False formulas are unprovable
One can easily replace (1) with either “False A is unprovable” or “True A is unprovable”.
(- +) = (-) (imaginary)
(+ +) = (+) (true)
(- -) = (+) (true)
(+ -) = (-) (imaginary)
The following is an explanation of what I am claiming here:
- We would get (- +) = (-) (imaginary) if A could be false and provable, which it cannot. False propositions cannot be proved true.
- We get the formula (+ +) = (+) (true) if it is true and provable.
- We get (- -) = (+) (true) if it is false and unprovable.
- Thus we get the formula (+ -) = (-) (imaginary) for the true and unprovable.
________________________________________________________________________________________
